#### What is a webserver?
We previously learned that TCP is a *transport layer protocol* that establishes a connection between a source and a destination server.
A webserver can listen on the http and https ports and can parse the requests on these ports.
Parsing is possible because http and https follow a standard:
``` Method(space)URL(space)Protocol header1: header1Value header2: header2Value header3: header3Value body ```We can create a webserver by creating a tcp socket and parsing the data we get from it.
```javascript
import net from "net";
const server = net.createServer((socket) => {
socket.on("data", (data) => {
const request = data.toString();
const [method, url] = request.split(" ");
const body = request.split("\r\n\r\n")[1];
if (url === "/") {
if (method === "GET") {
socket.write(
"HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\nContent-Type: text/plain\r\n\r\nHello World!\n"
);
socket.end();
}
if (method === "POST") {
// Do something with the body like adding it to a database
socket.write(
`HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\nContent-Type: text/plain\r\n\r\nValue added to the database\n`
);
socket.end();
}
}
});
});
```
---
#### Reverse and Forward proxy
It is more complex to handle requests in production.
Imagine you are receiving million of requests simultanously.
How will you webserver handle it?
Or imagine you would like to execute different processes based on the received request?
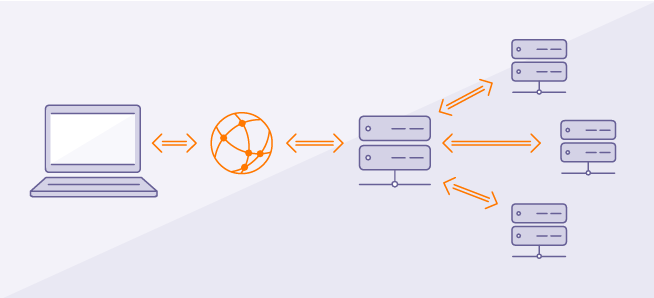
A common approach is to use a what we call a **reverse proxy** that will handle the incoming traffic and direct the requests to the appropriate process.
**Load balancing** is a kind of reverse proxy that is used to offload some of the request to different servers in case of high demand.
A process placed in front of backend processes is called a **gateway**.
Gateways can do many things, not just reverse proxy. they can do logging, security, auth, telemetry, etc..
`NGINX`, `Apache`, `Caddy` are webservers that are usually used in production as gateways.
##### Reverse proxy
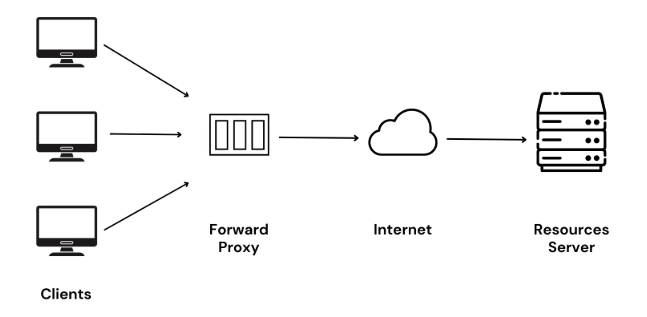
A forward proxy sits between the client and the internet and forward outgoing request on behalf of the client.
it can be used to:
1. Block allow specific sites
2. caching
3. anonymity ( hides the identity of the client)
4. by-pass geo restriction
##### Forward proxy
---
#### Systemd
Systemd provides a system and service manager that runs as PID 1 and starts the rest of the system.
In the above section we mentioned that our webserver was redirecting traffic to specific processes.
It is recommended to run these processes with systemd for the following reasons:
1. Automatic restart on failure
2. Cleaner way to stop a process (without leaving orphan processes)
3. Unified management (All your services — database, web server (e.g. Caddy), Node backend — are managed the same way)
To run a process with systemd we need to create a systemd service.
Here is an example of how to do it:
```bash
vim /etc/systemd/system/seniordevapi.service
```
```
# This is what comes in the seniordevapi.service file
Description=SeniorDev Backend Service
Documentation=https://nodejs.org/
After=network.target
[Service]
Type=simple
User=root
WorkingDirectory=/home/pilex/repos/SeniorDevBE
Environment=PATH=/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin
Environment=NODE_ENV=production # You can set any additional environment variables
ExecStart=/usr/bin/ts-node src/index.ts
Restart=on-failure
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
```
```bash
lsof -i :300
```
```bash
systemctl start seniordevapi.service
```